- What is the primary function of mitochondria in cellular respiration?
Answer: Mitochondria produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell, through cellular respiration. - Where does cellular respiration occur in eukaryotic cells?
Answer: Cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria. - What are the two main stages of cellular respiration that take place in the mitochondria?
Answer: The Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain. - What is the role of NADH and FADH2 in mitochondrial respiration?
Answer: They donate electrons to the electron transport chain to help produce ATP. - What is the significance of the mitochondrial inner membrane?
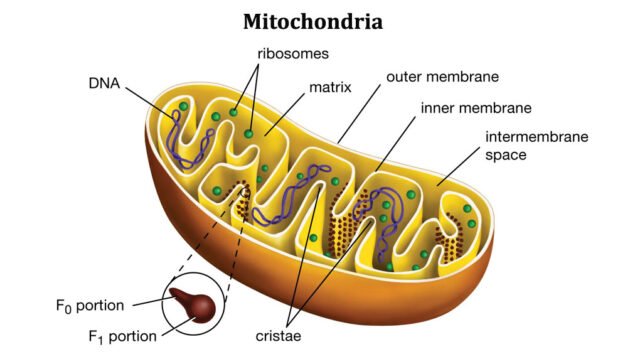
Answer: The inner membrane contains enzymes for the electron transport chain and ATP synthase, which are involved in ATP production. - Where does the Krebs cycle occur within the mitochondria?
Answer: The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. - What is the function of the electron transport chain in mitochondria?
Answer: It transfers electrons through protein complexes, releasing energy to pump protons across the membrane, creating a proton gradient for ATP synthesis. - What is the final electron acceptor in the mitochondrial electron transport chain?
Answer: Oxygen is the final electron acceptor, combining with electrons and protons to form water. - What molecule is produced in the mitochondrial matrix during the Krebs cycle?
Answer: ATP, NADH, FADH2, and carbon dioxide are produced during the Krebs cycle. - What is the role of ATP synthase in the mitochondria?
Answer: ATP synthase uses the proton gradient to synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. - How does the proton gradient contribute to ATP production?
Answer: The proton gradient across the inner membrane of the mitochondrion drives the production of ATP by ATP synthase. - What molecule enters the mitochondria to begin the Krebs cycle?
Answer: Acetyl-CoA enters the mitochondria and is used in the Krebs cycle. - What is the source of energy that powers the electron transport chain in mitochondria?
Answer: The energy comes from electrons carried by NADH and FADH2. - What is the function of oxygen in cellular respiration?
Answer: Oxygen serves as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain and helps produce water. - What is the main byproduct of mitochondrial cellular respiration?
Answer: The main byproducts are carbon dioxide and water. - What role do the cristae of the mitochondria play in cellular respiration?
Answer: The cristae increase the surface area for the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis. - Which type of phosphorylation occurs in the mitochondria?
Answer: Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the mitochondria during the electron transport chain. - What is the role of the mitochondrial matrix?
Answer: The mitochondrial matrix is where the Krebs cycle takes place, and it contains enzymes, substrates, and cofactors for respiration. - How many ATP molecules are typically produced from the complete oxidation of one glucose molecule in the mitochondria?
Answer: Typically, 32 to 34 ATP molecules are produced. - Which part of mitochondria contains its DNA and ribosomes?
Answer: The mitochondrial matrix contains the DNA and ribosomes. - What is produced during oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria?
Answer: ATP is produced during oxidative phosphorylation. - How do NADH and FADH2 contribute to ATP production in mitochondria?
Answer: NADH and FADH2 donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which drives proton pumping and ATP production. - Where does glycolysis take place, and what role does it play in mitochondrial respiration?
Answer: Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and produces pyruvate, which is transported into the mitochondria for further processing. - What is the role of the outer mitochondrial membrane?
Answer: The outer membrane acts as a barrier and regulates the entry and exit of molecules into and out of the mitochondrion. - What happens to the protons (H+) during the electron transport chain in mitochondria?
Answer: Protons are pumped from the matrix to the intermembrane space, creating a proton gradient. - How is ATP produced during the Krebs cycle?
Answer: ATP is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation during the Krebs cycle. - What molecule is required for the electron transport chain to function properly?
Answer: Oxygen is required as the final electron acceptor. - What is the significance of the mitochondrial DNA in cellular respiration?
Answer: Mitochondrial DNA encodes some of the proteins needed for mitochondrial function, including those involved in ATP production. - How does the ATP yield from anaerobic respiration compare to that of aerobic respiration in mitochondria?
Answer: Aerobic respiration yields much more ATP than anaerobic respiration. - What role does the mitochondrion play in energy metabolism beyond ATP production?
Answer: Mitochondria are involved in other metabolic processes such as apoptosis, calcium storage, and regulation of the cell cycle.
These questions and answers provide a comprehensive overview of the role of mitochondria in cellular respiration, helping to clarify key concepts and functions.