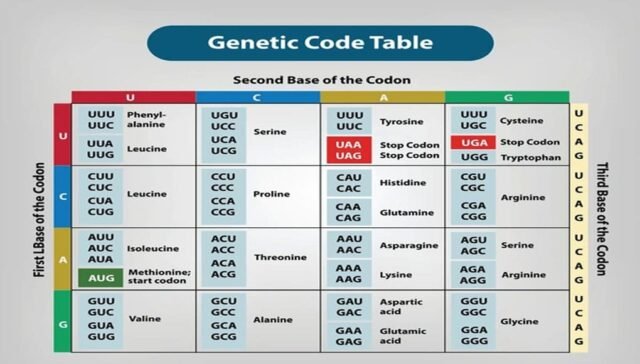
1. What does the term “genetic code” refer to?
a) The arrangement of genes in DNA
b) The set of rules by which nucleotide sequences are translated into proteins
c) The composition of amino acids in proteins
d) The structure of DNA molecules
Answer: b) The set of rules by which nucleotide sequences are translated into proteins
2. How many codons are present in the genetic code?
a) 20
b) 64
c) 61
d) 3
Answer: b) 64
3. Which codon serves as the start codon in most organisms?
a) UAA
b) AUG
c) UAG
d) UGA
Answer: b) AUG
4. What does the genetic code being “degenerate” mean?
a) One codon codes for multiple amino acids
b) Multiple codons code for the same amino acid
c) The code is prone to mutations
d) The code changes over time
Answer: b) Multiple codons code for the same amino acid
5. Which of the following are stop codons?
a) AUG and UGA
b) UAA, UAG, and UGA
c) UAA and AUG
d) UGA and UUU
Answer: b) UAA, UAG, and UGA
6. The genetic code is universal because:
a) It varies across different organisms
b) The same codon codes for the same amino acid in all organisms
c) It is unique to humans
d) It is identical in viruses and humans
Answer: b) The same codon codes for the same amino acid in all organisms
7. Which amino acid is coded by the start codon AUG?
a) Glycine
b) Methionine
c) Alanine
d) Proline
Answer: b) Methionine
8. How many codons code for amino acids?
a) 64
b) 61
c) 20
d) 3
Answer: b) 61
9. What is the function of stop codons in protein synthesis?
a) Initiate translation
b) Terminate translation
c) Add amino acids
d) Start RNA synthesis
Answer: b) Terminate translation
10. Which nucleotide triplet is NOT a stop codon?
a) UAA
b) UAG
c) AUG
d) UGA
Answer: c) AUG
11. Why is the genetic code non-overlapping?
a) Codons are read one at a time without overlap
b) Each nucleotide is part of multiple codons
c) Adjacent codons share nucleotides
d) Some codons are skipped during translation
Answer: a) Codons are read one at a time without overlap
12. Which amino acid is coded by the codon UUU?
a) Phenylalanine
b) Leucine
c) Lysine
d) Valine
Answer: a) Phenylalanine
13. What is the key feature of the genetic code being “triplet”?
a) Each codon is made up of three amino acids
b) Three codons are read simultaneously
c) Each codon is made up of three nucleotides
d) Every three amino acids form a codon
Answer: c) Each codon is made up of three nucleotides
14. How is the genetic code read during translation?
a) In groups of two nucleotides
b) Continuously in triplets without punctuation
c) Randomly across the mRNA
d) In overlapping patterns
Answer: b) Continuously in triplets without punctuation
15. What property of the genetic code prevents ambiguity?
a) Degeneracy
b) Universality
c) Each codon codes for only one amino acid
d) Wobble pairing
Answer: c) Each codon codes for only one amino acid
16. What is the wobble hypothesis related to?
a) Multiple start codons in the genetic code
b) Flexibility in base pairing at the third codon position
c) Overlapping genes in DNA
d) Misfolding of proteins during synthesis
Answer: b) Flexibility in base pairing at the third codon position
17. How many stop codons exist in the genetic code?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Answer: c) 3
18. Which of these is not a feature of the genetic code?
a) Degenerate
b) Universal
c) Ambiguous
d) Triplet
Answer: c) Ambiguous
19. Which type of RNA carries the codon sequence?
a) tRNA
b) rRNA
c) mRNA
d) hnRNA
Answer: c) mRNA
20. What does “non-overlapping code” ensure in translation?
a) Unique reading frames for codons
b) Repeated reading of codons
c) Misreading of codons
d) Skipping certain codons
Answer: a) Unique reading frames for codons
21. What is the anticodon for the codon UAC?
a) AUG
b) UGU
c) GUA
d) AUA
Answer: a) AUG
22. Which scientist(s) discovered the structure of the genetic code?
a) Watson and Crick
b) Nirenberg and Khorana
c) Griffith
d) Franklin and Wilkins
Answer: b) Nirenberg and Khorana
23. What amino acid does the codon GAA code for?
a) Glutamic acid
b) Glycine
c) Glutamine
d) Alanine
Answer: a) Glutamic acid
24. How is the genetic code “commaless”?
a) Codons overlap in the sequence
b) Codons are read without gaps or punctuation
c) Stop codons act as commas
d) Splicing introduces commas
Answer: b) Codons are read without gaps or punctuation
25. Which of the following is a synonymous codon pair?
a) UUU and UCU
b) AUG and UAA
c) GAA and GAG
d) UGA and UGG
Answer: c) GAA and GAG
26. Which codon specifies tryptophan?
a) UGG
b) UGA
c) UGU
d) UGC
Answer: a) UGG
27. Why is the genetic code nearly universal?
a) It is identical in all organisms except mitochondria and some protozoans
b) It applies only to eukaryotes
c) Codons vary widely across species
d) It applies only to proteins of higher organisms
Answer: a) It is identical in all organisms except mitochondria and some protozoans
28. What does degeneracy in the genetic code help prevent?
a) Silent mutations affecting protein function
b) Frameshift mutations
c) Amino acid misfolding
d) Codon redundancy
Answer: a) Silent mutations affecting protein function
29. What is the role of the AUG codon besides starting translation?
a) It serves as a stop codon
b) It codes for methionine
c) It codes for all amino acids
d) It acts as a splice site
Answer: b) It codes for methionine
30. How does the degeneracy of the genetic code contribute to evolution?
a) Increases mutation rates
b) Allows flexibility in coding sequences
c) Causes protein misfolding
d) Reduces genetic diversity
Answer: b) Allows flexibility in coding sequences