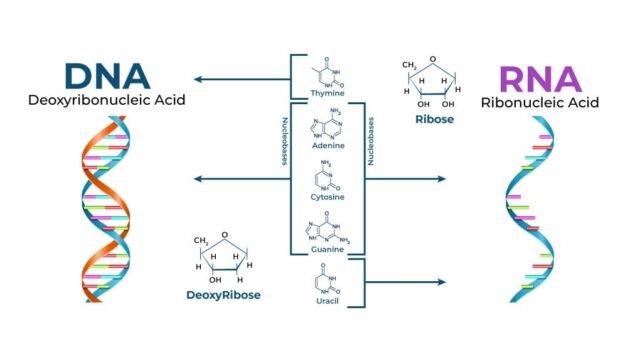
1. Basic Structure
- Which sugar is found in the structure of DNA?
- A) Glucose
- B) Ribose
- C) Deoxyribose
- D) Fructose
Answer: C) Deoxyribose
- What type of sugar is present in RNA?
- A) Ribose
- B) Deoxyribose
- C) Maltose
- D) Sucrose
Answer: A) Ribose
- How many strands does DNA have?
- A) Single-stranded
- B) Double-stranded
- C) Triple-stranded
- D) Quadruple-stranded
Answer: B) Double-stranded
- What type of strand is RNA?
- A) Single-stranded
- B) Double-stranded
- C) Helical
- D) Circular
Answer: A) Single-stranded
- Which nitrogenous base is unique to DNA?
- A) Uracil
- B) Adenine
- C) Thymine
- D) Cytosine
Answer: C) Thymine
2. Nitrogenous Bases
- Which base in RNA pairs with adenine?
- A) Thymine
- B) Cytosine
- C) Guanine
- D) Uracil
Answer: D) Uracil
- What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA?
- A) Adenine, Guanine, Uracil, Cytosine
- B) Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
- C) Thymine, Uracil, Adenine, Guanine
- D) Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine
Answer: B) Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
- Which base is absent in RNA?
- A) Thymine
- B) Cytosine
- C) Guanine
- D) Uracil
Answer: A) Thymine
3. Functions of DNA and RNA
- What is the primary function of DNA?
- A) Protein synthesis
- B) Genetic information storage
- C) Energy production
- D) Transport of molecules
Answer: B) Genetic information storage
- What is the main function of RNA?
- A) DNA replication
- B) Genetic information storage
- C) Protein synthesis
- D) Energy transfer
Answer: C) Protein synthesis
- Which type of RNA carries the genetic code from DNA?
- A) mRNA
- B) tRNA
- C) rRNA
- D) siRNA
Answer: A) mRNA
- What does tRNA do in protein synthesis?
- A) Stores genetic information
- B) Carries amino acids to ribosomes
- C) Translates RNA into DNA
- D) Forms ribosomes
Answer: B) Carries amino acids to ribosomes
4. Chemical Differences
- Which molecule is more chemically stable?
- A) DNA
- B) RNA
Answer: A) DNA
- Why is RNA less stable than DNA?
- A) Double-stranded structure
- B) Ribose sugar has an extra hydroxyl group
- C) No thymine base
- D) Shorter length
Answer: B) Ribose sugar has an extra hydroxyl group
- What type of bond connects nucleotides in both DNA and RNA?
- A) Hydrogen bonds
- B) Ionic bonds
- C) Phosphodiester bonds
- D) Peptide bonds
Answer: C) Phosphodiester bonds
5. Types of RNA
- Which type of RNA is a structural component of ribosomes?
- A) mRNA
- B) rRNA
- C) tRNA
- D) miRNA
Answer: B) rRNA
- Which RNA type regulates gene expression?
- A) tRNA
- B) rRNA
- C) miRNA
- D) mRNA
Answer: C) miRNA
6. Biological Significance
- Why is DNA replication essential?
- A) Energy production
- B) Genetic material transmission to offspring
- C) Protein modification
- D) Nutrient metabolism
Answer: B) Genetic material transmission to offspring
- What enables RNA to perform catalytic functions?
- A) Its double-stranded nature
- B) Its hydroxyl group
- C) Its ability to form 3D structures
- D) Its pairing with DNA
Answer: C) Its ability to form 3D structures
- What is the significance of the uracil base in RNA?
- A) Provides stability to RNA
- B) Replaces thymine in RNA
- C) Enhances protein synthesis
- D) Increases replication rate
Answer: B) Replaces thymine in RNA
7. Laboratory Applications
- Which technique is used to amplify DNA?
- A) PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
- B) RT-PCR
- C) Gel Electrophoresis
- D) Western Blotting
Answer: A) PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
- Which process converts RNA back into DNA?
- A) Transcription
- B) Reverse Transcription
- C) Translation
- D) DNA replication
Answer: B) Reverse Transcription
- Which molecule is studied in transcriptomics?
- A) DNA
- B) RNA
- C) Proteins
- D) Lipids
Answer: B) RNA
8. Evolutionary Insights
- Which molecule is thought to have evolved first?
- A) DNA
- B) RNA
Answer: B) RNA
- What hypothesis suggests RNA\u2019s early role in life?
- A) Central Dogma Hypothesis
- B) RNA World Hypothesis
- C) Double Helix Hypothesis
- D) Gene Theory
Answer: B) RNA World Hypothesis
9. Key Comparisons
- Which is more prone to mutations?
- A) DNA
- B) RNA
Answer: B) RNA
- Which molecule can self-replicate under experimental conditions?
- A) DNA
- B) RNA
Answer: B) RNA
- Where is DNA primarily located?
- A) Cytoplasm
- B) Nucleus
- C) Ribosomes
- D) Cell membrane
Answer: B) Nucleus
- Where is RNA found in the cell?
- A) Nucleus
- B) Cytoplasm
- C) Ribosomes
- D) All of the above
Answer: D) All of the above
- What feature distinguishes DNA from RNA structurally and functionally?
- A) Single vs. Double Strand
- B) Stability and Longevity
- C) Base Composition
- D) All of the above
Answer: D) All of the above