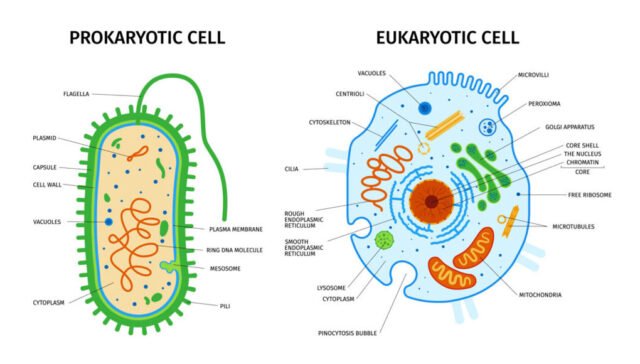
1. What is the primary difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- Answer: Prokaryotic cells lack a membrane-bound nucleus, whereas eukaryotic cells have a defined, membrane-bound nucleus.
2. Do prokaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles?
- Answer: No, prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles.
3. What type of DNA is found in prokaryotic cells?
- Answer: Prokaryotic cells have a single, circular DNA molecule located in the nucleoid region.
4. What type of DNA is found in eukaryotic cells?
- Answer: Eukaryotic cells have linear DNA that is organized within a membrane-bound nucleus.
5. Are prokaryotic cells smaller than eukaryotic cells?
- Answer: Yes, prokaryotic cells are typically smaller, usually ranging from 0.2 to 2 micrometers in size.
6. What structures do both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share?
- Answer: Both types of cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes.
7. Do eukaryotic cells have a nucleus?
- Answer: Yes, eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus.
8. Where is the genetic material located in prokaryotic cells?
- Answer: In prokaryotic cells, genetic material is located in the nucleoid region, which is not membrane-bound.
9. What is a key feature of the cell wall in prokaryotic cells?
- Answer: The cell wall in prokaryotic cells is composed of peptidoglycan.
10. What is the cell wall made of in plant eukaryotic cells?
- Answer: The cell wall in plant eukaryotic cells is made of cellulose.
11. Do prokaryotic cells have mitochondria?
- Answer: No, prokaryotic cells lack mitochondria.
12. Which organelles are found in eukaryotic cells but not in prokaryotic cells?
- Answer: Eukaryotic cells have organelles like mitochondria, the Golgi apparatus, and the endoplasmic reticulum, which are absent in prokaryotic cells.
13. What is the role of ribosomes in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- Answer: Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
14. How do prokaryotic cells divide?
- Answer: Prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission.
15. How do eukaryotic cells divide?
- Answer: Eukaryotic cells divide through mitosis or meiosis.
16. Do prokaryotic cells have chloroplasts?
- Answer: No, prokaryotic cells do not have chloroplasts. However, some prokaryotes like cyanobacteria can perform photosynthesis.
17. Do eukaryotic cells have flagella?
- Answer: Yes, eukaryotic cells can have flagella, but they are structurally different from those in prokaryotic cells.
18. What is the shape of prokaryotic cells?
- Answer: Prokaryotic cells can be spherical (cocci), rod-shaped (bacilli), or spiral (spirilla).
19. Do prokaryotic cells have a cytoskeleton?
- Answer: Prokaryotic cells have a simple cytoskeleton, but it is not as complex as the one in eukaryotic cells.
20. Which type of cell can be multicellular?
- Answer: Eukaryotic cells can be multicellular, forming multicellular organisms like plants, animals, and fungi.
21. Are prokaryotic cells unicellular or multicellular?
- Answer: Prokaryotic cells are unicellular organisms.
22. What is the function of the plasma membrane in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- Answer: The plasma membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell and provides structural support.
23. Do eukaryotic cells contain a nucleolus?
- Answer: Yes, eukaryotic cells contain a nucleolus within the nucleus, which is involved in ribosome production.
24. Can prokaryotic cells perform cellular respiration?
- Answer: Yes, prokaryotic cells perform cellular respiration, but it occurs across the plasma membrane rather than in mitochondria.
25. Which type of cells have plasmids?
- Answer: Prokaryotic cells often contain plasmids, which are small, circular DNA molecules.
26. Do eukaryotic cells have a Golgi apparatus?
- Answer: Yes, eukaryotic cells have a Golgi apparatus, which processes and packages proteins.
27. Do prokaryotic cells have a Golgi apparatus?
- Answer: No, prokaryotic cells lack a Golgi apparatus.
28. What is the main function of the cell wall in prokaryotic cells?
- Answer: The cell wall in prokaryotic cells provides structural support, shape, and protection.
29. What is a characteristic feature of the ribosomes in prokaryotic cells?
- Answer: Prokaryotic cells have smaller (70S) ribosomes compared to the larger (80S) ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells.
30. Which type of cells have a more complex internal structure?
- Answer: Eukaryotic cells have a more complex internal structure due to the presence of membrane-bound organelles.
These short questions and answers offer a clear comparison between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, helping students understand their differences for exams.