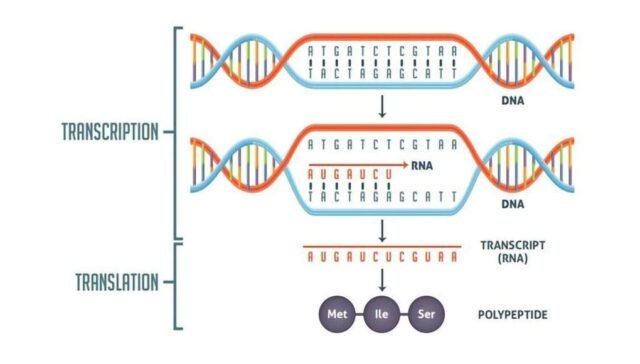
1. What is the first step of transcription?
a) RNA processing
b) RNA polymerase binding to the promoter
c) Elongation of the RNA strand
d) Termination of transcription
Answer: b) RNA polymerase binding to the promoter
2. Which molecule is transcribed from DNA during transcription?
a) mRNA
b) tRNA
c) rRNA
d) All of the above
Answer: a) mRNA
3. Which enzyme is responsible for synthesizing RNA during transcription?
a) DNA polymerase
b) RNA polymerase
c) Ligase
d) Helicase
Answer: b) RNA polymerase
4. Where does transcription occur in eukaryotic cells?
a) Cytoplasm
b) Nucleus
c) Mitochondria
d) Ribosome
Answer: b) Nucleus
5. Which of the following is NOT involved in the process of transcription?
a) RNA polymerase
b) Ribosomes
c) Promoter
d) DNA template
Answer: b) Ribosomes
6. What does mRNA stand for?
a) Messenger RNA
b) Membrane RNA
c) Micro RNA
d) Mitochondrial RNA
Answer: a) Messenger RNA
7. Which of the following is a modification made to mRNA after transcription in eukaryotic cells?
a) Addition of a poly-A tail
b) Removal of exons
c) Binding of ribosomes
d) Addition of a protein cap
Answer: a) Addition of a poly-A tail
8. Which type of RNA carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome?
a) tRNA
b) mRNA
c) rRNA
d) snRNA
Answer: b) mRNA
9. What is the function of ribosomes in translation?
a) To synthesize DNA
b) To synthesize proteins from mRNA
c) To carry amino acids
d) To modify RNA
Answer: b) To synthesize proteins from mRNA
10. Which part of the ribosome is responsible for binding with mRNA?
a) Large subunit
b) Small subunit
c) A site
d) P site
Answer: b) Small subunit
11. During translation, tRNA carries which of the following to the ribosome?
a) Amino acids
b) mRNA
c) rRNA
d) DNA
Answer: a) Amino acids
12. What is the sequence of three bases on mRNA called that specifies an amino acid?
a) Codon
b) Anticodon
c) Exon
d) Intron
Answer: a) Codon
13. Which of the following is the start codon for translation?
a) UAA
b) UGA
c) AUG
d) UGC
Answer: c) AUG
14. What is the role of the tRNA anticodon?
a) To bind with the ribosome
b) To carry amino acids to the ribosome
c) To pair with the mRNA codon
d) To catalyze the formation of peptide bonds
Answer: c) To pair with the mRNA codon
15. Which of the following is involved in both transcription and translation?
a) Ribosomes
b) mRNA
c) RNA polymerase
d) DNA
Answer: b) mRNA
16. Where does translation occur in eukaryotic cells?
a) Nucleus
b) Cytoplasm
c) Endoplasmic reticulum
d) Mitochondria
Answer: b) Cytoplasm
17. What is the function of the promoter region in transcription?
a) It binds RNA polymerase and signals the start of transcription
b) It signals the end of transcription
c) It holds the DNA strands together
d) It modifies the RNA after transcription
Answer: a) It binds RNA polymerase and signals the start of transcription
18. What happens to the mRNA after transcription in prokaryotes?
a) It is processed by splicing
b) It is immediately translated into proteins
c) It is transported to the nucleus
d) It undergoes post-transcriptional modifications
Answer: b) It is immediately translated into proteins
19. Which of the following statements about translation is true?
a) It takes place inside the nucleus
b) Ribosomes link amino acids together to form proteins
c) DNA is directly involved in translation
d) Only mRNA is involved in translation
Answer: b) Ribosomes link amino acids together to form proteins
20. In eukaryotic cells, which of the following processes occurs in the nucleus?
a) Translation
b) Transcription
c) mRNA processing
d) Both b and c
Answer: d) Both b and c
21. Which molecule contains the instructions for building proteins?
a) mRNA
b) tRNA
c) rRNA
d) DNA
Answer: a) mRNA
22. What is the end product of translation?
a) DNA
b) RNA
c) Protein
d) Amino acids
Answer: c) Protein
23. In which direction does RNA polymerase read the DNA template during transcription?
a) 5′ to 3′
b) 3′ to 5′
c) 3′ to 3′
d) 5′ to 5′
Answer: b) 3′ to 5′
24. Which of the following is NOT a step in translation?
a) Elongation
b) Initiation
c) Splicing
d) Termination
Answer: c) Splicing
25. What type of bond is formed between amino acids during translation?
a) Hydrogen bond
b) Phosphodiester bond
c) Peptide bond
d) Ionic bond
Answer: c) Peptide bond
26. What is the function of the ribosome’s A site during translation?
a) It holds the tRNA with the growing peptide chain
b) It holds the mRNA
c) It receives incoming tRNA carrying an amino acid
d) It releases the finished protein
Answer: c) It receives incoming tRNA carrying an amino acid
27. Which process requires the help of RNA polymerase?
a) Replication
b) Transcription
c) Translation
d) Splicing
Answer: b) Transcription
28. In which phase of translation are amino acids linked together?
a) Initiation
b) Elongation
c) Termination
d) Transcription
Answer: b) Elongation
29. Which of the following is the final product of transcription?
a) mRNA
b) tRNA
c) rRNA
d) Protein
Answer: a) mRNA
30. What happens during the termination phase of translation?
a) A stop codon is recognized and the polypeptide is released
b) The ribosome moves along the mRNA
c) mRNA is spliced
d) A new tRNA enters the ribosome
Answer: a) A stop codon is recognized and the polypeptide is released
These MCQs offer a comprehensive understanding of the transcription and translation processes and their key components.