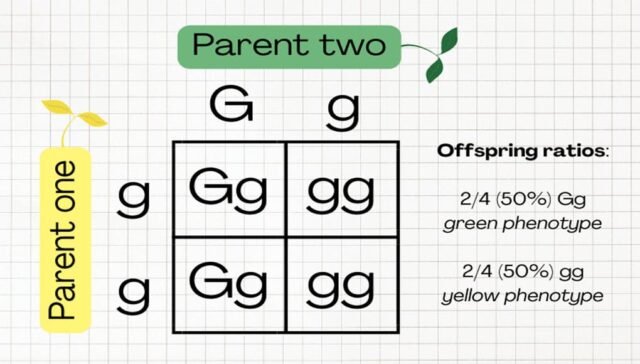
1. What is the purpose of a Punnett square?
A) To study the inheritance of traits
B) To track genetic mutations
C) To visualize offspring genotypes from parental crosses
D) To calculate the number of genes in a genome
Answer: C) To visualize offspring genotypes from parental crosses
2. What does a Punnett square represent?
A) The probability of a genetic mutation
B) The physical traits of offspring
C) The likelihood of gene combinations in offspring
D) The number of chromosomes inherited
Answer: C) The likelihood of gene combinations in offspring
3. What are the two components that are placed on the top and side of a Punnett square?
A) Dominant and recessive alleles
B) Genotype and phenotype
C) Parental gametes
D) Genes and traits
Answer: C) Parental gametes
4. If a homozygous dominant parent (AA) is crossed with a homozygous recessive parent (aa), what will the offspring genotype ratio be?
A) 100% Aa
B) 50% Aa, 50% aa
C) 50% AA, 50% aa
D) 100% AA
Answer: A) 100% Aa
5. In a Punnett square, the F1 generation results from the combination of which two types of gametes?
A) Two recessive alleles
B) Two dominant alleles
C) Two parental gametes
D) Two dominant and two recessive alleles
Answer: C) Two parental gametes
6. In a monohybrid cross between two heterozygous individuals (Bb x Bb), what is the probability of the offspring being homozygous dominant (BB)?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
Answer: B) 25%
7. If a plant with the genotype Bb is crossed with another plant of genotype Bb, what is the expected genotype ratio of the offspring?
A) 1 BB : 2 Bb : 1 bb
B) 1 BB : 1 Bb
C) 2 BB : 2 bb
D) 1 Bb : 2 bb
Answer: A) 1 BB : 2 Bb : 1 bb
8. In a Punnett square, what do the letters on the left and top represent?
A) Dominant alleles
B) Recessive alleles
C) The genotype of the offspring
D) The gametes of the parents
Answer: D) The gametes of the parents
9. What type of cross involves two individuals who are both heterozygous for two traits?
A) Monohybrid cross
B) Dihybrid cross
C) Test cross
D) Back cross
Answer: B) Dihybrid cross
10. If two heterozygous individuals for a single trait are crossed (Aa x Aa), what is the expected phenotypic ratio?
A) 1 dominant : 1 recessive
B) 3 dominant : 1 recessive
C) 2 dominant : 2 recessive
D) 1 dominant : 2 recessive
Answer: B) 3 dominant : 1 recessive
11. When two purebred plants with different traits are crossed, what is the expected phenotype ratio in the F1 generation?
A) 100% of one trait
B) 1:1 ratio
C) 50% dominant and 50% recessive traits
D) 100% of the dominant trait
Answer: D) 100% of the dominant trait
12. In a Punnett square for a dihybrid cross, what do the 16 squares represent?
A) The phenotypic ratio
B) The genotypic ratio
C) Possible combinations of alleles in the offspring
D) Parental genotypes
Answer: C) Possible combinations of alleles in the offspring
13. If a person with blood type AB (genotype AB) marries someone with blood type O (genotype OO), what is the probability of their child having blood type A?
A) 25%
B) 50%
C) 75%
D) 100%
Answer: B) 50%
14. What is a key difference between a test cross and a Punnett square cross?
A) Test cross involves a homozygous recessive individual
B) Test cross involves both heterozygous individuals
C) Test cross is used to find phenotypic ratios
D) There is no difference
Answer: A) Test cross involves a homozygous recessive individual
15. In a dihybrid cross, if the two genes assort independently, what is the ratio of phenotypes in the F2 generation?
A) 1:1
B) 3:1
C) 9:3:3:1
D) 1:2:1
Answer: C) 9:3:3:1
16. How many possible genotypes can be produced from a cross between a heterozygous (Bb) and a homozygous dominant (BB) individual?
A) One genotype
B) Two genotypes
C) Three genotypes
D) Four genotypes
Answer: B) Two genotypes
17. What is the expected genotypic ratio from a cross between two heterozygous individuals for a single trait (Aa x Aa)?
A) 1 AA : 2 Aa : 1 aa
B) 1 AA : 1 Aa
C) 2 AA : 2 aa
D) 3 Aa : 1 aa
Answer: A) 1 AA : 2 Aa : 1 aa
18. If a plant with genotype Aa is crossed with another plant of genotype Aa, what is the probability that the offspring will inherit two recessive alleles (aa)?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
Answer: B) 25%
19. What is the phenotypic ratio for a monohybrid cross between two heterozygous parents (Aa x Aa)?
A) 1:1
B) 3:1
C) 2:1
D) 4:0
Answer: B) 3:1
20. If a homozygous dominant (RR) is crossed with a homozygous recessive (rr), what is the genotype of the F1 offspring?
A) All Rr
B) All rr
C) All RR
D) All Rr and rr
Answer: A) All Rr
21. What is the purpose of the Punnett square when dealing with multiple traits?
A) To find the parental traits
B) To show the inheritance of one gene
C) To calculate the likelihood of different genotype combinations
D) To find the dominant allele
Answer: C) To calculate the likelihood of different genotype combinations
22. If the two genes are linked, what will be the expected result in a Punnett square for a dihybrid cross?
A) 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio
B) A skewed phenotypic ratio closer to the parental traits
C) A 3:1 phenotypic ratio
D) The ratio will be completely random
Answer: B) A skewed phenotypic ratio closer to the parental traits
23. In a Punnett square, what is represented in the boxes of the square?
A) Phenotypes
B) Genotypes of the offspring
C) Parental gametes
D) Dominant alleles
Answer: B) Genotypes of the offspring
24. Which of the following describes a dihybrid Punnett square?
A) It involves two traits and four possible gamete combinations
B) It involves one trait and two possible gamete combinations
C) It tracks one allele combination
D) It only involves recessive traits
Answer: A) It involves two traits and four possible gamete combinations
25. In a monohybrid cross, the offspring genotypes of a heterozygous (Bb) x homozygous recessive (bb) cross will produce what ratio?
A) 1 BB : 1 Bb
B) 2 Bb : 2 bb
C) 1 Bb : 1 bb
D) 3 Bb : 1 bb
Answer: C) 1 Bb : 1 bb
26. If a cross between two heterozygous individuals (Bb x Bb) for a single trait results in a 1:2:1 genotypic ratio, what is the expected phenotypic ratio?
A) 1:1
B) 3:1
C) 2:1
D) 4:0
Answer: B) 3:1
27. When solving for genetic problems involving multiple traits, which type of Punnett square is used?
A) Monohybrid square
B) Dihybrid square
C) Test cross square
D) Triple square
Answer: B) Dihybrid square
28. What will the offspring phenotype be if two homozygous dominant plants (RR) are crossed?
A) 100% recessive trait
B) 100% dominant trait
C) 50% dominant and 50% recessive
D) 75% dominant and 25% recessive
Answer: B) 100% dominant trait
29. What does a Punnett square allow scientists to calculate?
A) The probability of genetic mutations
B) The genotype of the parents
C) The genetic variation in a population
D) The likelihood of an offspring having a particular genotype or phenotype
Answer: D) The likelihood of an offspring having a particular genotype or phenotype
30. In a test cross, what genotype would the homozygous recessive parent have?
A) Aa
B) AA
C) Aa or AA
D) aa
Answer: D) aa
These MCQs cover a range of topics related to Punnett squares and genetics, allowing students to test their understanding of Mendelian inheritance patterns and the applications of Punnett squares in predicting genetic outcomes.