Arthritis
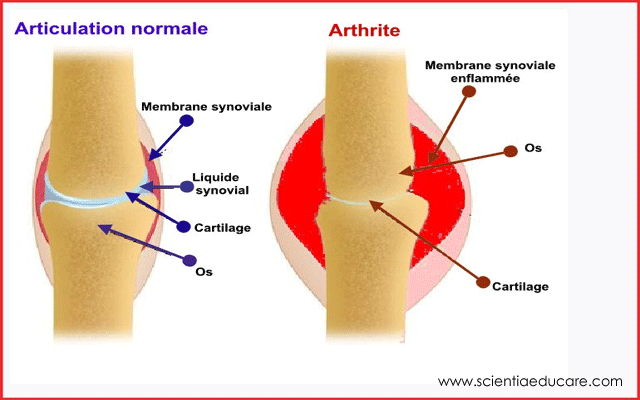
Arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammation of the joints. It can affect one joint or multiple joints. There are more than 100 different types of arthritis,...
Cancer
Cancer
Cancer, also called malignancy, is an abnormal growth of cells. There are more than 100 types of cancer, including breast cancer, skin cancer, lung...
Heart Disease
Heart Disease
Heart disease describes a range of conditions that affect your heart. Diseases under the heart disease umbrella include blood vessel diseases, such as...
Ureters
Ureters
The ureters are a pair of small tubes that connect the kidneys to the urinary bladder. They form a vital link in the urinary...
Tongue
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of most vertebrates that manipulates food for mastication, and is used in the act of...
Thyroid
Thyroid
Through the hormones it produces, the thyroid gland influences almost all of the metabolic processes in your body. Thyroid disorders can range from a...
Stomach
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular organ located on the left side of the upper abdomen. The stomach receives food from the esophagus. As food...
Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, fragile tubelike structure that begins at the end of the brain stem and continues down almost to...
Small Intestine
Small Intestine
The small intestine is a tubular structure within the abdominal cavity that carries the food in continuation with the stomach up to the...
Skin
Skin
The skin is the largest organ of the body, with a total area of about 20 square feet. The skin protects us from microbes...
Pituitary Gland
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland is a pea-sized structure located at the base of the brain, just below the hypothalamus, to which it is attached...
Parathyroid Glands
Parathyroid Glands
A number of vital functions in human body are controlled by biochemical substances, called hormones, which are chemical messengers released by either ductless...
Pancreas
Pancreas
The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal...
Nose
Nose
Nose Parts
The nose has two holes called nostrils. The nostrils and the nasal passages are separated by a wall called the septum (say: SEP-tum)....
Mouth
Mouth
In human anatomy, the mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food and saliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous...
Lungs
Lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of respiration in humans and many other animals including a few fish and some snails. In mammals and...
Liver
Liver
The liver is a large, meaty organ that sits on the right side of the belly. Weighing about 3 pounds, the liver is reddish-brown...
Larynx (voice box)
Larynx (voice box)
Laryngeal cancer is not as well known by the general public as some other types of cancer, yet it is not a...
Large Intestine
Large Intestine
The large intestine is the final section of the gastrointestinal tract that performs the vital task of absorbing water and vitamins while converting...
Kidneys
Kidneys
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs found on the left and right sides of the body in vertebrates. They filter the blood in order...