Summary
Periodic Classification of Elements
• The grouping of elements with similar properties together and the separation of elements with dissimilar properties is known as classification of elements. The table, which classifies elements on the basis of their properties, is called the periodic table.
• The earliest classification was into metals and non-metals, which was on the basis of physical and chemical properties.

• Dobereiner’s Triads arranged elements in an increasing order of atomic mass, in groups of three. The atomic mass of the middle element was the arithmetic mean of the other two elements of the triad.

• Newland’s law of octaves states that on arranging elements in increasing order of their atomic mass, the eighth element resembles the first in physical and chemical properties, just like the eighth node on a musical scale resembles the first note.

• The law could only be applied upto calcium. No vacant spaces were left for undiscovered elements.
• According to Mendeleev’s periodic law, the physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic mass.
• Mendeleev was able to predict the existence of undiscovered elements like Ga, Sc and Ge.
• Mendeleev corrected the atomic masses of a few elements on the basis of their positions in the periodic table.
• Mendeleev’s table could not assign a proper position to hydrogen or to the lanthanides and actinides and isotopes.

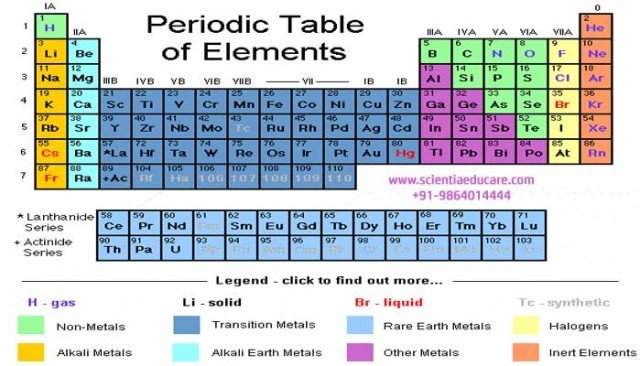
• Modern periodic law states that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. It is based on electronic configuration of the elements.
• The vertical columns are called groups, while the horizontal rows are called periods.

• There are 7 periods and 8 groups subdivided into 18 sub groups.
• Group number is number of electrons in the valence shell. Elements having the same valence number are grouped together.
• The number of shells present in the atom gives period number.
• The noble gases are on the extreme right of the table and on the table’s extreme left, are the alkali metals.

• d- Block elements are the elements of group 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12 placed in the middle of the table. They are also known as transition elements.

• The inner transition or f-Block elements – lanthanides and actinides, are placed in two separate horizontal series at the bottom of the periodic table.

• s-Block elements are the elements of group 1 and 2. p- Block elements are the elements of groups 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 and 18.
• Ionization potential (I.P) is the energy required to remove the outermost electron from an isolated gaseous atom of an element.
• Ionization potential increases along the period and decreases down the group. Be, Mg, N, P and noble gases have exceptionally high values of ionization potential due to their stable electronic configurations.
• Electron affinity (E.A) is the energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom of an element. It increases along the period and decreases down the group.

• Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a molecule of a compound. It increases from left to right in each period.


• Metallic character decreases along a period and increases down a group.
• Valency of an element with respect to hydrogen increases from 1 to 4 and then falls from 4 to 1 across a period.
• Valency of an element with respect to oxygen increases from 1 to 7 along a period.
Best Wishes From www.scientiaeducare.com
Helping you choose a successful career….