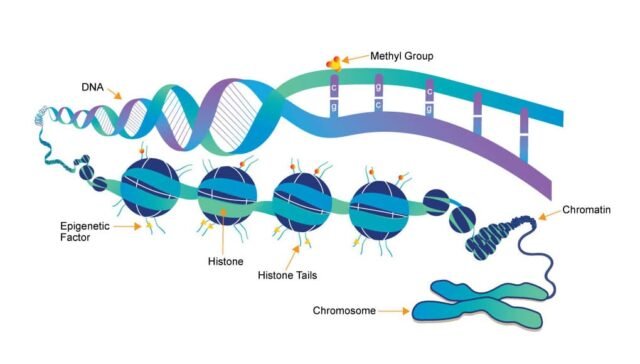
1. What is epigenetics?
a) Changes in the DNA sequence
b) Inherited traits passed through genetic mutations
c) Changes in gene expression without altering the DNA sequence
d) The study of mutations in the genome
Answer: c) Changes in gene expression without altering the DNA sequence
2. Which of the following is NOT an example of an epigenetic modification?
a) DNA methylation
b) Histone modification
c) Gene duplication
d) Non-coding RNA regulation
Answer: c) Gene duplication
3. Which of the following chemical modifications is associated with gene silencing?
a) Histone acetylation
b) DNA methylation
c) Histone methylation
d) Both b and c
Answer: d) Both b and c
4. What is the role of DNA methylation in gene expression?
a) It activates gene expression
b) It inhibits gene expression
c) It neutralizes gene expression
d) It has no effect on gene expression
Answer: b) It inhibits gene expression
5. Which enzyme is responsible for adding methyl groups to DNA?
a) DNA methylase
b) DNA polymerase
c) Histone deacetylase
d) RNA polymerase
Answer: a) DNA methylase
6. Histone acetylation typically results in:
a) Gene repression
b) Chromatin condensation
c) Gene activation
d) Chromatin tightening
Answer: c) Gene activation
7. What is the effect of histone acetylation on chromatin structure?
a) Condensation of chromatin
b) Loosening of chromatin
c) Tightening of DNA coils
d) No change in chromatin structure
Answer: b) Loosening of chromatin
8. Which of the following is a key characteristic of heterochromatin?
a) It is transcriptionally active
b) It is highly condensed
c) It is loosely packed
d) It contains very few genes
Answer: b) It is highly condensed
9. What is the role of non-coding RNAs in epigenetics?
a) They code for proteins
b) They modify histones
c) They regulate gene expression by silencing specific mRNAs
d) They directly alter DNA sequences
Answer: c) They regulate gene expression by silencing specific mRNAs
10. X-inactivation in females is an example of:
a) Genetic mutation
b) Epigenetic regulation
c) Gene amplification
d) DNA replication
Answer: b) Epigenetic regulation
11. What is the term for epigenetic modifications that are passed down to offspring?
a) Transcriptional regulation
b) Heritable epigenetic changes
c) Genetic mutations
d) Post-translational modifications
Answer: b) Heritable epigenetic changes
12. Which of the following is a common consequence of DNA methylation in mammals?
a) Activation of tumor suppressor genes
b) Inactivation of specific genes
c) Gene duplication
d) Increase in chromatin structure
Answer: b) Inactivation of specific genes
13. Which non-coding RNA is involved in RNA interference?
a) tRNA
b) miRNA
c) rRNA
d) mRNA
Answer: b) miRNA
14. What is genomic imprinting?
a) A process by which both copies of a gene are active
b) A reversible epigenetic phenomenon where the expression of a gene depends on its parental origin
c) The alteration of DNA sequence by mutations
d) The activation of genes in the presence of certain environmental factors
Answer: b) A reversible epigenetic phenomenon where the expression of a gene depends on its parental origin
15. Which of the following is a major player in the process of X-inactivation?
a) miRNA
b) XIST RNA
c) siRNA
d) mRNA
Answer: b) XIST RNA
16. Which of the following epigenetic modifications can lead to the development of cancer?
a) DNA methylation
b) Histone deacetylation
c) Both a and b
d) Gene mutation
Answer: c) Both a and b
17. Which of the following is true about the epigenetic modifications in identical twins?
a) Their epigenetic profiles are identical throughout life
b) Environmental factors can lead to differences in epigenetic modifications
c) Their epigenetic profiles do not change over time
d) They have no epigenetic differences at birth
Answer: b) Environmental factors can lead to differences in epigenetic modifications
18. Which enzyme removes acetyl groups from histones?
a) Histone acetyltransferase (HAT)
b) Histone deacetylase (HDAC)
c) DNA methyltransferase
d) RNA polymerase
Answer: b) Histone deacetylase (HDAC)
19. Which of the following best describes the concept of epigenetic plasticity?
a) The ability of an organism’s genetic makeup to change over time
b) The ability of epigenetic changes to influence gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence
c) The formation of new genetic mutations
d) The inability of cells to revert to previous gene expression states
Answer: b) The ability of epigenetic changes to influence gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence
20. Which of the following is a potential therapeutic approach for diseases caused by epigenetic changes?
a) Gene therapy
b) Histone modification inhibitors
c) Antibiotic treatment
d) Dietary supplements
Answer: b) Histone modification inhibitors
21. What does the term “epigenetic memory” refer to?
a) The genetic mutations that accumulate over generations
b) The ability of cells to inherit specific gene expression states after cell division
c) The process of gene replication
d) The process of DNA sequencing in cells
Answer: b) The ability of cells to inherit specific gene expression states after cell division
22. What role do small RNA molecules, such as siRNAs, play in epigenetics?
a) They transcribe DNA into RNA
b) They catalyze the formation of histone modifications
c) They degrade target mRNA and inhibit gene expression
d) They enhance DNA replication
Answer: c) They degrade target mRNA and inhibit gene expression
23. Which process is considered a form of epigenetic regulation of gene expression in plants?
a) Gene duplication
b) RNA editing
c) DNA methylation and histone modifications
d) Point mutations
Answer: c) DNA methylation and histone modifications
24. Which of the following is an example of environmental factors affecting epigenetic regulation?
a) Changes in the DNA sequence due to mutations
b) Changes in protein synthesis rates
c) Diet, toxins, and stress leading to epigenetic changes
d) Protein folding and stability
Answer: c) Diet, toxins, and stress leading to epigenetic changes
25. Which of the following epigenetic changes is most commonly associated with aging?
a) Gene mutation
b) Histone modification
c) DNA replication errors
d) Telomere lengthening
Answer: b) Histone modification
26. What is the effect of DNA demethylation on gene expression?
a) It activates gene expression
b) It silences gene expression
c) It has no effect on gene expression
d) It alters the DNA sequence
Answer: a) It activates gene expression
27. Which of the following conditions could result from abnormal epigenetic regulation?
a) Cystic fibrosis
b) Hemophilia
c) Cancer
d) Down syndrome
Answer: c) Cancer
28. What does the process of “epigenetic reprogramming” involve?
a) Changing the DNA sequence of an organism
b) Resetting epigenetic markers in germline cells and early embryos
c) Producing non-coding RNAs
d) Changing protein synthesis pathways
Answer: b) Resetting epigenetic markers in germline cells and early embryos
29. Which of the following is a key mechanism in the regulation of gene expression in the brain?
a) DNA replication
b) Epigenetic modifications
c) mRNA splicing
d) Genetic mutations
Answer: b) Epigenetic modifications
30. Which of the following diseases has been linked to epigenetic changes in gene expression?
a) Alzheimer’s disease
b) Cystic fibrosis
c) Down syndrome
d) Hemophilia
Answer: a) Alzheimer’s disease
These MCQs provide a comprehensive overview of key concepts in epigenetics, touching upon mechanisms, modifications, and their implications for health and disease.