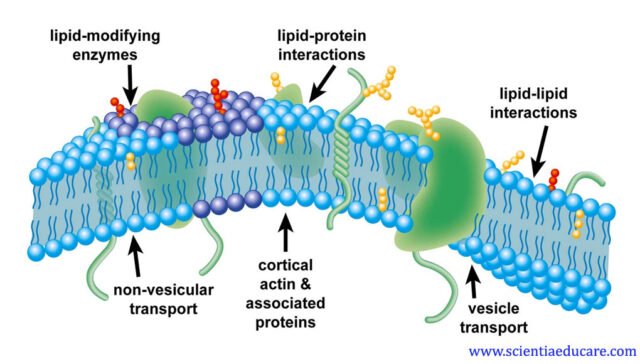
1. Which of the following best describes the primary structure of the plasma membrane?
A) A single lipid layer
B) A bilayer of phospholipids
C) A network of proteins
D) A triple layer of phospholipids
Answer: B) A bilayer of phospholipids
2. Which component is mainly responsible for the selective permeability of the plasma membrane?
A) Phospholipids
B) Cholesterol
C) Membrane proteins
D) Carbohydrates
Answer: C) Membrane proteins
3. What is the function of cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
A) Facilitates cell communication
B) Provides structural stability and fluidity
C) Acts as a transport channel
D) Contributes to the immune response
Answer: B) Provides structural stability and fluidity
4. What are the structures embedded in the plasma membrane that allow for transport of molecules?
A) Phospholipids
B) Receptor proteins
C) Transport proteins
D) Carbohydrates
Answer: C) Transport proteins
5. The process by which large particles are engulfed by the cell membrane is called:
A) Diffusion
B) Phagocytosis
C) Active transport
D) Exocytosis
Answer: B) Phagocytosis
6. Which of the following is true for facilitated diffusion?
A) It requires energy (ATP)
B) It uses protein channels to move substances
C) It moves substances against the concentration gradient
D) It only occurs in plant cells
Answer: B) It uses protein channels to move substances
7. Which type of transport requires the use of ATP to move substances across the plasma membrane?
A) Passive diffusion
B) Facilitated diffusion
C) Active transport
D) Osmosis
Answer: C) Active transport
8. The sodium-potassium pump is an example of:
A) Passive transport
B) Active transport
C) Simple diffusion
D) Osmosis
Answer: B) Active transport
9. Osmosis refers to the movement of:
A) Water from low to high concentration
B) Water from high to low concentration
C) Solutes from high to low concentration
D) Solutes from low to high concentration
Answer: B) Water from high to low concentration
10. Which of the following substances can pass through the plasma membrane most easily?
A) Glucose
B) Oxygen
C) Sodium ions
D) Proteins
Answer: B) Oxygen
11. The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane suggests that:
A) The membrane is rigid and impermeable
B) The membrane components are fixed in place
C) The membrane has a static structure
D) The membrane components move freely within the layer
Answer: D) The membrane components move freely within the layer
12. Which of the following statements about diffusion is correct?
A) Diffusion requires energy input
B) Diffusion moves molecules from high to low concentration
C) Diffusion only occurs in liquids
D) Diffusion moves substances against the concentration gradient
Answer: B) Diffusion moves molecules from high to low concentration
13. Which of the following types of molecules cannot pass through the plasma membrane without the help of transport proteins?
A) Oxygen
B) Carbon dioxide
C) Glucose
D) Water
Answer: C) Glucose
14. Which type of solution causes a cell to swell due to water intake?
A) Isotonic
B) Hypotonic
C) Hypertonic
D) None of the above
Answer: B) Hypotonic
15. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of active transport?
A) Requires energy
B) Moves substances against the concentration gradient
C) Involves transport proteins
D) Occurs without ATP
Answer: D) Occurs without ATP
16. What is the role of glycoproteins in the plasma membrane?
A) Serve as transport channels
B) Aid in cell recognition
C) Provide structural support
D) Regulate fluidity
Answer: B) Aid in cell recognition
17. Which of the following types of transport requires a channel or carrier protein but does not require energy?
A) Active transport
B) Facilitated diffusion
C) Osmosis
D) Endocytosis
Answer: B) Facilitated diffusion
18. Exocytosis is the process by which:
A) Cells take in particles via engulfment
B) Molecules exit the cell in vesicles
C) Water enters the cell
D) Small ions move through a channel protein
Answer: B) Molecules exit the cell in vesicles
19. The process of endocytosis is used for:
A) The transport of water into the cell
B) The engulfment of large particles
C) Moving ions against the concentration gradient
D) Expelling waste from the cell
Answer: B) The engulfment of large particles
20. What is the function of receptor proteins in the plasma membrane?
A) Provide structural integrity to the membrane
B) Facilitate the movement of water
C) Detect specific molecules and initiate cell responses
D) Store energy for the cell
Answer: C) Detect specific molecules and initiate cell responses
21. Which of the following occurs during phagocytosis?
A) Liquid droplets are ingested
B) Large particles are engulfed by the cell membrane
C) Small ions are transported via proteins
D) A vesicle merges with the plasma membrane
Answer: B) Large particles are engulfed by the cell membrane
22. What is the result of a cell being placed in a hypertonic solution?
A) The cell will swell
B) The cell will shrink
C) The cell will remain the same size
D) Water will enter the cell
Answer: B) The cell will shrink
23. Which of the following is an example of a membrane-bound organelle involved in transport?
A) Ribosome
B) Mitochondrion
C) Golgi apparatus
D) Nucleus
Answer: C) Golgi apparatus
24. What is the primary role of the plasma membrane?
A) Energy production
B) Protein synthesis
C) Regulation of what enters and exits the cell
D) DNA storage
Answer: C) Regulation of what enters and exits the cell
25. Which of the following best describes the characteristic of a membrane’s selective permeability?
A) It allows all molecules to pass freely
B) It restricts the passage of only large molecules
C) It permits some molecules to pass while restricting others
D) It allows no molecules to pass
Answer: C) It permits some molecules to pass while restricting others
26. Which mechanism does a cell use to take in dissolved substances from the extracellular fluid?
A) Phagocytosis
B) Pinocytosis
C) Osmosis
D) Active transport
Answer: B) Pinocytosis
27. What is the function of the sodium-potassium pump?
A) Transport sodium ions into the cell and potassium ions out
B) Transport glucose into the cell
C) Move water across the plasma membrane
D) Maintain osmotic balance within the cell
Answer: A) Transport sodium ions into the cell and potassium ions out
28. Which of the following is true about the plasma membrane’s lipid bilayer?
A) It is permeable to most polar molecules
B) It is permeable to nonpolar molecules
C) It prevents the passage of nonpolar molecules
D) It is impermeable to gases like oxygen
Answer: B) It is permeable to nonpolar molecules
29. Which transport mechanism moves molecules from low to high concentration?
A) Facilitated diffusion
B) Active transport
C) Simple diffusion
D) Osmosis
Answer: B) Active transport
30. The process by which water molecules move across the plasma membrane is called:
A) Diffusion
B) Active transport
C) Osmosis
D) Exocytosis
Answer: C) Osmosis
These questions cover key concepts related to the structure, function, and transport mechanisms of the plasma membrane, which are crucial for students studying cell biology.