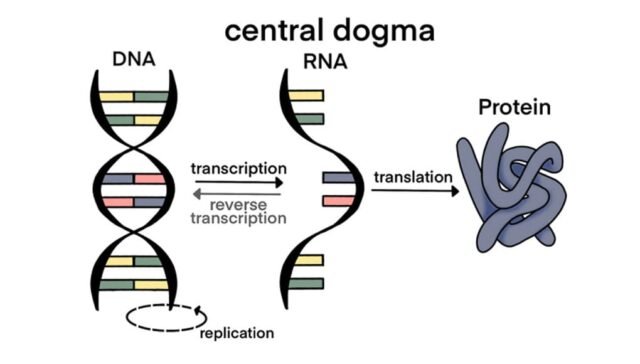
- What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
- A) DNA to RNA to Protein
- B) Protein to RNA to DNA
- C) RNA to DNA to Protein
- D) DNA to Protein to RNA
- Answer: A) DNA to RNA to Protein
- Which process converts DNA to RNA?
- A) Translation
- B) Transcription
- C) Replication
- D) Protein synthesis
- Answer: B) Transcription
- What is the process of converting RNA into protein called?
- A) Transcription
- B) Replication
- C) Translation
- D) Splicing
- Answer: C) Translation
- What molecule is synthesized during transcription?
- A) mRNA
- B) tRNA
- C) rRNA
- D) DNA
- Answer: A) mRNA
- Where does transcription occur in eukaryotic cells?
- A) Cytoplasm
- B) Mitochondria
- C) Nucleus
- D) Ribosomes
- Answer: C) Nucleus
- Which enzyme is responsible for transcription in cells?
- A) RNA polymerase
- B) DNA polymerase
- C) Ligase
- D) Helicase
- Answer: A) RNA polymerase
- Which of the following is NOT involved in translation?
- A) mRNA
- B) tRNA
- C) Ribosomes
- D) DNA polymerase
- Answer: D) DNA polymerase
- What is the primary function of ribosomes in translation?
- A) To synthesize RNA
- B) To assemble amino acids into proteins
- C) To replicate DNA
- D) To transcribe genes
- Answer: B) To assemble amino acids into proteins
- What does tRNA carry during translation?
- A) Amino acids
- B) mRNA
- C) DNA
- D) Ribosomes
- Answer: A) Amino acids
- Which type of RNA carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome?
- A) rRNA
- B) mRNA
- C) tRNA
- D) snRNA
- Answer: B) mRNA
- What happens during the process of transcription?
- A) DNA is replicated
- B) RNA is synthesized from a DNA template
- C) Proteins are made
- D) tRNA is synthesized
- Answer: B) RNA is synthesized from a DNA template
- What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
- A) It unzips the DNA double helix
- B) It catalyzes the formation of mRNA from DNA
- C) It binds to ribosomes
- D) It synthesizes proteins
- Answer: B) It catalyzes the formation of mRNA from DNA
- In eukaryotes, where does the mRNA undergo processing before it leaves the nucleus?
- A) It is transcribed into rRNA
- B) Introns are removed, and exons are spliced together
- C) It is translated into protein
- D) It is replicated
- Answer: B) Introns are removed, and exons are spliced together
- Which sequence of bases in mRNA is responsible for specifying an amino acid?
- A) Codon
- B) Anticodon
- C) Promoter
- D) Terminator
- Answer: A) Codon
- What is the function of the ribosome during translation?
- A) To decode mRNA and synthesize proteins
- B) To synthesize RNA from DNA
- C) To replicate DNA
- D) To transport amino acids
- Answer: A) To decode mRNA and synthesize proteins
- In the process of translation, which molecule pairs with the mRNA codon?
- A) Ribosome
- B) tRNA
- C) RNA polymerase
- D) DNA
- Answer: B) tRNA
- What happens to mRNA after translation is complete?
- A) It is degraded
- B) It is replicated
- C) It becomes part of the ribosome
- D) It enters the nucleus
- Answer: A) It is degraded
- Which of the following is a correct sequence of events in protein synthesis?
- A) Replication → Transcription → Translation
- B) Transcription → Replication → Translation
- C) Transcription → Translation → Replication
- D) Translation → Transcription → Replication
- Answer: C) Transcription → Translation → Replication
- What is the sequence of three bases in tRNA that is complementary to the mRNA codon called?
- A) Exon
- B) Codon
- C) Anticodon
- D) Promoter
- Answer: C) Anticodon
- What is the purpose of the promoter region in DNA?
- A) It signals the end of transcription
- B) It binds to RNA polymerase to initiate transcription
- C) It attaches to ribosomes for translation
- D) It codes for amino acids
- Answer: B) It binds to RNA polymerase to initiate transcription
- In prokaryotes, where does transcription occur?
- A) Nucleus
- B) Mitochondria
- C) Cytoplasm
- D) Ribosome
- Answer: C) Cytoplasm
- Which of the following molecules is involved in both transcription and translation?
- A) rRNA
- B) DNA
- C) mRNA
- D) tRNA
- Answer: C) mRNA
- What determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein?
- A) The sequence of nucleotides in DNA
- B) The sequence of nucleotides in RNA
- C) The ribosome structure
- D) The codons in mRNA
- Answer: A) The sequence of nucleotides in DNA
- What is the function of the 5′ cap and poly-A tail in eukaryotic mRNA?
- A) They help the mRNA bind to the ribosome and protect it from degradation
- B) They assist in the transcription process
- C) They help mRNA splice introns
- D) They encode the amino acid sequence
- Answer: A) They help the mRNA bind to the ribosome and protect it from degradation
- Which of the following is true about DNA replication and transcription?
- A) Both processes produce RNA
- B) Replication produces a DNA strand, while transcription produces RNA
- C) Transcription requires DNA polymerase
- D) Replication occurs in the ribosome
- Answer: B) Replication produces a DNA strand, while transcription produces RNA
- What happens to the mRNA after it is transcribed in the nucleus?
- A) It is translated into protein in the ribosome
- B) It is spliced and processed before leaving the nucleus
- C) It is stored in the nucleus
- D) It is replicated
- Answer: B) It is spliced and processed before leaving the nucleus
- In prokaryotic cells, what is the site of translation?
- A) Nucleus
- B) Cytoplasm
- C) Mitochondria
- D) Ribosome
- Answer: B) Cytoplasm
- Which sequence in the DNA does RNA polymerase recognize to start transcription?
- A) Exon
- B) Introns
- C) Promoter
- D) Terminator
- Answer: C) Promoter
- What is the main function of messenger RNA (mRNA)?
- A) To bring amino acids to the ribosome
- B) To carry genetic information from DNA to the ribosome
- C) To form part of the ribosome
- D) To catalyze protein synthesis
- Answer: B) To carry genetic information from DNA to the ribosome
- What is the role of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase in translation?
- A) It catalyzes the binding of the tRNA to the mRNA
- B) It adds the correct amino acid to the tRNA molecule
- C) It assembles the ribosome
- D) It initiates transcription
- Answer: B) It adds the correct amino acid to the tRNA molecule
Home Biology Topics with MCQs Molecular Biology MCQs on the “Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: DNA to Protein”