MCQs and answers on “Advances in Cancer Biology: Mechanisms and Therapies”
1. What is the most common cause of cancer?
a) Environmental factors
b) Genetic mutations
c) Age-related changes
d) Diet
Answer: b) Genetic mutations
2. Which gene is known as...
Unveiling the Human Microbiome: A Hidden World That Shapes Health and Disease
Introduction
The human body is home to a complex and dynamic ecosystem of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and archaea. These microbes, collectively known as...
Questions on the topic “Human Microbiome: Its Role in Health and Disease”
1. What is the human microbiome and how does it affect our health?
Answer:
The human microbiome refers to the collection of trillions of microorganisms, including...
MCQs on the topic “Human Microbiome: Its Role in Health and Disease”
1. Which of the following is the primary function of the human microbiome?
a) Digestion of food
b) Immune system regulation
c) Synthesis of...
Pathogen
Pathogen
We normally think of pathogens in hostile terms—as invaders that attack our bodies. But a pathogen or a parasite, like any other organism, is...
Coronary heart diseaseOsteoporosisAllergy
Coronary heart diseaseOsteoporosisAllergy
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is an age dependent disorder with loss of the normal density of bone.
The bones become fragile and are easily fractured. Bones...
Diabetes mellitusCardio vascular diseasesHypertension
Diabetes mellitusCardio vascular diseasesHypertension
Diabetes mellitus and hypertension are interrelated diseases that strongly predispose an individual to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.1 2 An estimated 3 million...
Filariasis
Filariasis
Symptoms of filariasis are dependent on species and body type and can be acute or chronic in nature. Up to 70% of infected individuals...
Diphtheria
Diphtheria
Diphtheria is a serious bacterial infection that affects the mucous membranes of the throat and nose. Although it spreads easily from one person to...
TyphoidCholera
TyphoidCholera
Cholera is an acute infectious disease caused by Vibrio cholerae bacteria. The disease is transmitted through contaminated water and food. When a patient’s stool...
MeaslesChicken poxInfluenzaTuberculosis
MeaslesChicken poxInfluenzaTuberculosis
Tuberculosis, or TB, is still one of the major causes of preventable death in the world. TB is an infectious disease caused by...
Poliomylitis
Poliomylitis
Polio (also known as poliomyelitis) is a highly contagious disease caused by a virus that attacks the nervous system. Children younger than 5 years...
Rabies
Rabies
Rabies is a life-threatening condition that causes tens of thousands of deaths worldwide every year. Dogs are the most common source.
It’s caused by a...
Hepatitis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis refers to an inflammatory condition of the liver. It’s commonly caused by a viral infection, but there are other possible causes of hepatitis....
Dangue
Dangue
The Dengue Fever is a mosquito borne disease, and over the years, it has become an increasingly common phenomenon in developing nations. The dengue...
Malaria
Malaria
Malaria is a serious, sometimes fatal, disease spread by mosquitoes and caused by a parasite. Malaria was a significant health risk in the U.S....
AIDS
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV/AIDS weakens a person's ability to fight infections. It is contracted through unprotected...
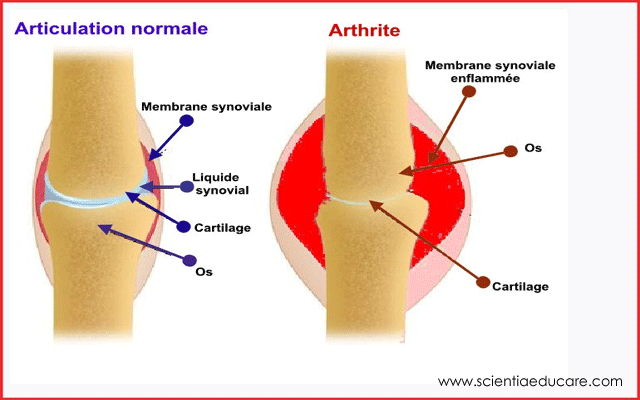
Arthritis
Arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammation of the joints. It can affect one joint or multiple joints. There are more than 100 different types of arthritis,...
Cancer
Cancer
Cancer, also called malignancy, is an abnormal growth of cells. There are more than 100 types of cancer, including breast cancer, skin cancer, lung...
Heart Disease
Heart Disease
Heart disease describes a range of conditions that affect your heart. Diseases under the heart disease umbrella include blood vessel diseases, such as...